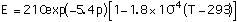 (1)
(1)
Lithium aluminate (LiAlO2) is a candidate tritium breeding material for a D-T fusion power plant blanket.
DATA AND CORRELATIONS
The thermal and physical properties of lithium aluminate are from refs [1, 2]. Correlations of the thermal and structural properties as functions of temperature are as follows:
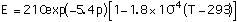 (1)
(1)
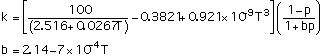 (2)
(2)
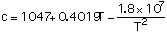 (3)
(3)
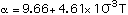 (4)
(4)
with p the porosity and all temperatures in degrees K. These equations are valid in the temperature range of 300-1100 K. The coefficient b in Eq 2 is assumed to be the same as that for lithium oxide.
Figures 1-2 show the variation of properties with temperature and Figs 3-4 show the effect of porosity on the thermal conductivity and elastic modulus.
TABLE 1 Thermal and Structural Properties of lithium aluminate
T K [[rho]] E GPa [[nu]] k W/m-K c J/kg-K [[sigma]]y [[alpha]]
kg/m3 MPa (10-6)
m/m-K
300 2600.0 209.735 9.143 967.569 11.043
350 207.845 8.088 1040.726 11.273
400 205.955 7.254 1095.260 11.504
450 204.065 6.583 1138.966 11.734
500 202.175 6.035 1175.950 11.965
550 200.285 5.584 1208.541 12.195
600 198.395 5.211 1238.140 12.426
650 196.505 4.903 1265.631 12.656
700 194.615 4.649 1291.595 12.887
750 192.725 4.442 1316.425 13.117
800 190.835 4.277 1340.395 13.348
850 188.945 4.150 1363.702 13.578
900 187.055 4.056 1386.488 13.809
950 185.165 3.994 1408.860 14.039
1000 183.275 3.961 1430.900 14.270
1050 181.385 3.957 1452.668 14.500
1100 179.495 3.979 1474.214 14.731
1150 177.605 4.028 1495.574 14.961
1200 175.715 4.103 1516.780 15.192
k (W/m-K) c (J/kg-K)
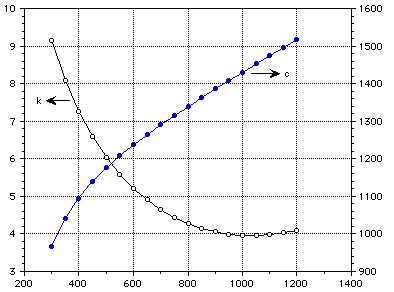
Temperature (K)
Figure 1: Thermal conductivity and specific heat of lithium aluminate.
E (GPa) [[alpha]] (10-6 m/m-K)
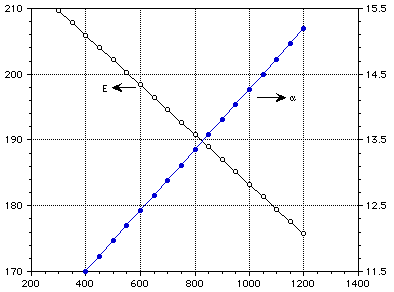
Temperature (K)
Figure 2: Elastic modulus and thermal expansion of lithium aluminate.
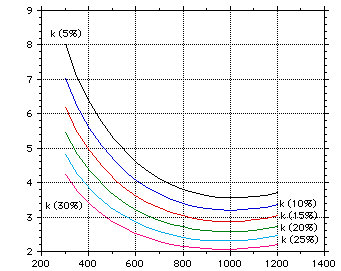
Temperature (K)
Figure 3 : The effect of porosity on the thermal conductivity of lithium aluminate.
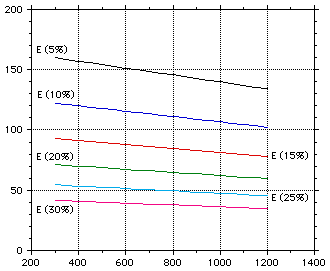
Temperature (K)
Figure 4 : The effect of porosity on the elastic modulus of lithium aluminate.